Models & Assays
Using the ARTE10 (APP-PS1) Mouse Model at 5 Months (In Collaboration with Taconic Biosciences)
Early Alzheimer’s Biomarkers: Using the ARTE10 (APP-PS1) Mouse Model at 5 Months
The ARTE10 double transgenic mouse model, which expresses mutant forms of human APP (Swedish mutation) and human Presenilin 1 carrying the M146 mutation (PSEN1), serves as a translational preclinical model for studying Alzheimer's disease. Despite its potential, there is limited data available on various behavioral assays and relevant biomarkers across different time points in the ARTE10 model.
Our aim is to behaviorally and biochemically characterize the ARTE10 model across three time points, corresponding to early, middle, and late stages of amyloid progression. Currently, we present data from the first time point at 5 months of age.
At 5 months of age, ARTE10 mice exhibit increased anxiety-like behaviors, hyperactivity, deficits in sensory motor gating, and spatial working memory deficits. Additionally, these mice show biomarkers relevant to Alzheimer's disease, including increased amyloid load in the hippocampus and cortex, and trending differences in NfL and cytokines. Data at 10 months of age is coming soon!
Sensory motor gating- Prepulse inhibition (PPI)
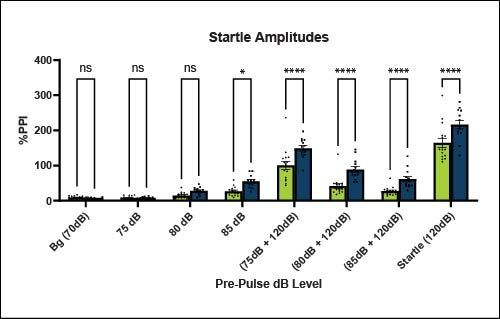
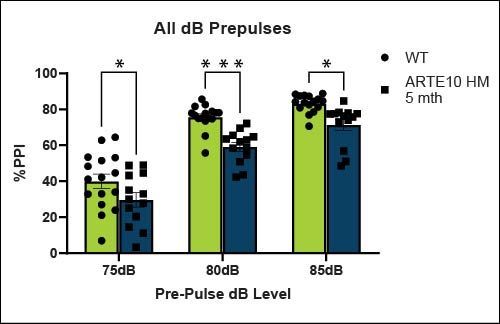
Homozygous ARTE10 animals have an increased startle response and reduced PPI indicating deficits in sensory motor-gating compared to WT controls
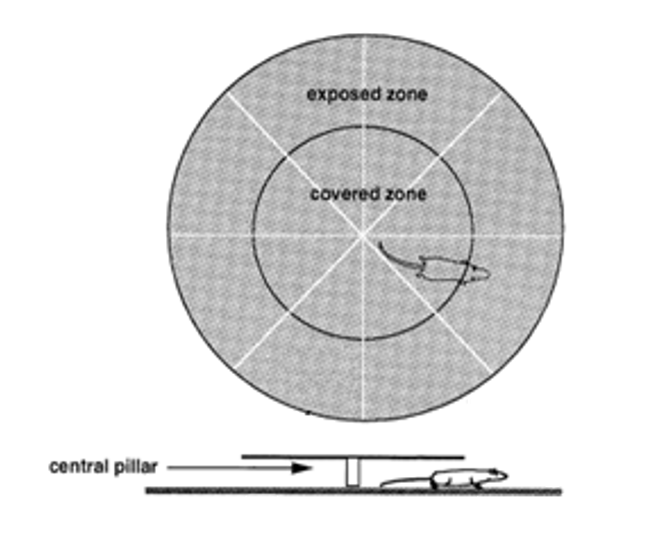
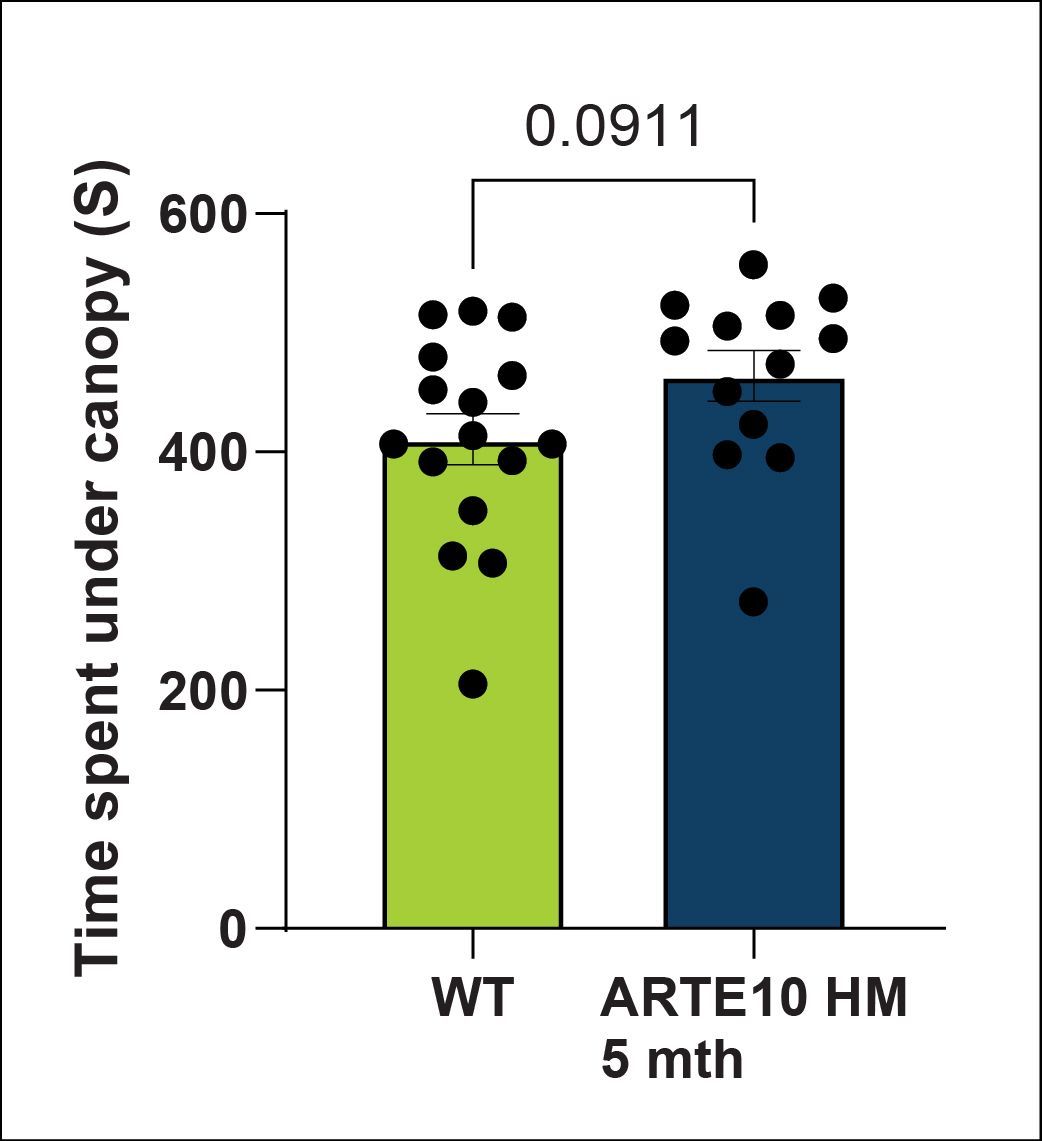
Anxiety-like Behavior - Canopy Test
Anxiety-like behaviours are detected in homozygous ARTE10 animals at 5 months of age using the canopy test1. ARTE10 animals also perform less risk-taking behaviours such as looking over the edge of the canopy maze.


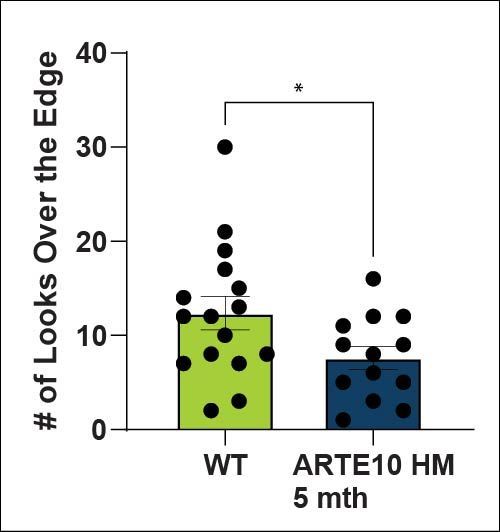
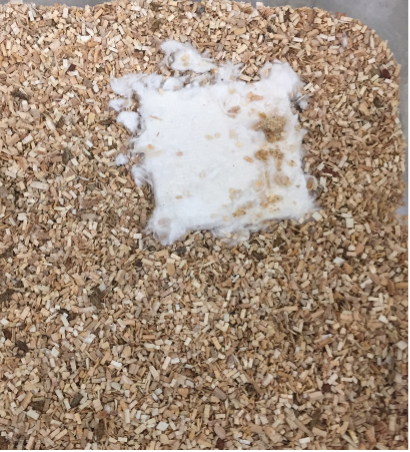
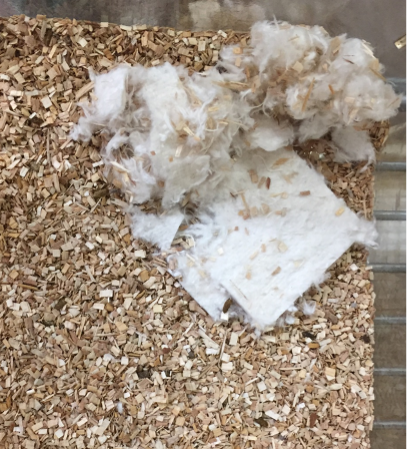
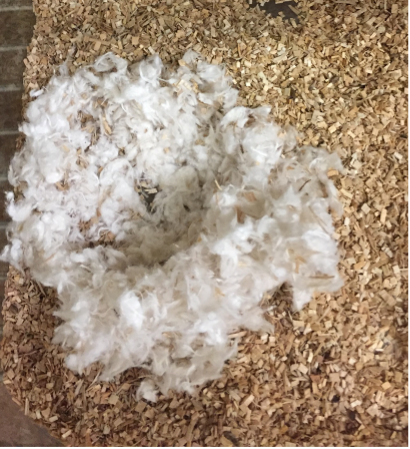
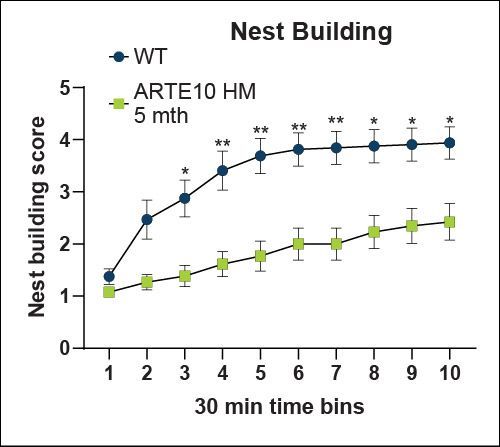
Well-being-like Behavior - Nest Building
Nest complexity is indicative of an animal’s mood, motivation and well-being. ARTE10 animals do not build nests as complex as WT controls supporting a mood disturbance in these animals2.



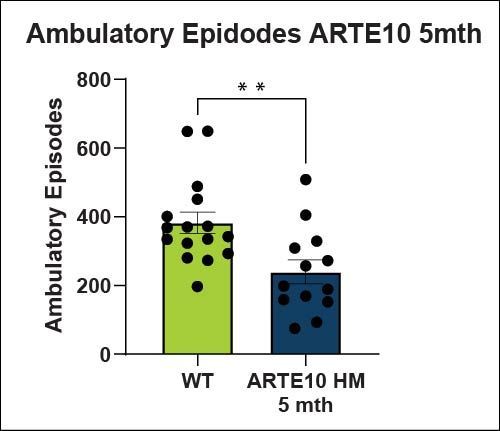
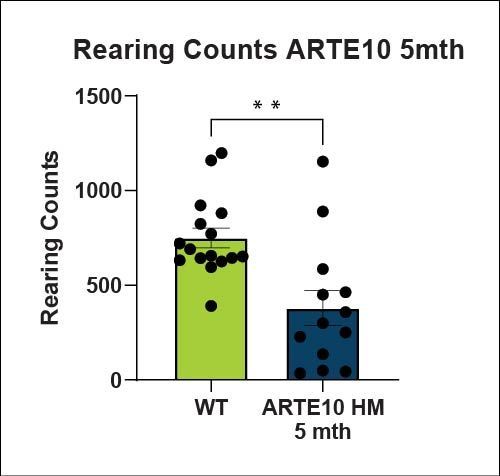
Motor Function - Locomotor Activity (LMA)
Hypolocomotion in ARTE10 mice, is likely due to increased anxiety-like behavior in a novel environment. Animals prefer the outer edges and corners compared to the open center as shown in the path plots.


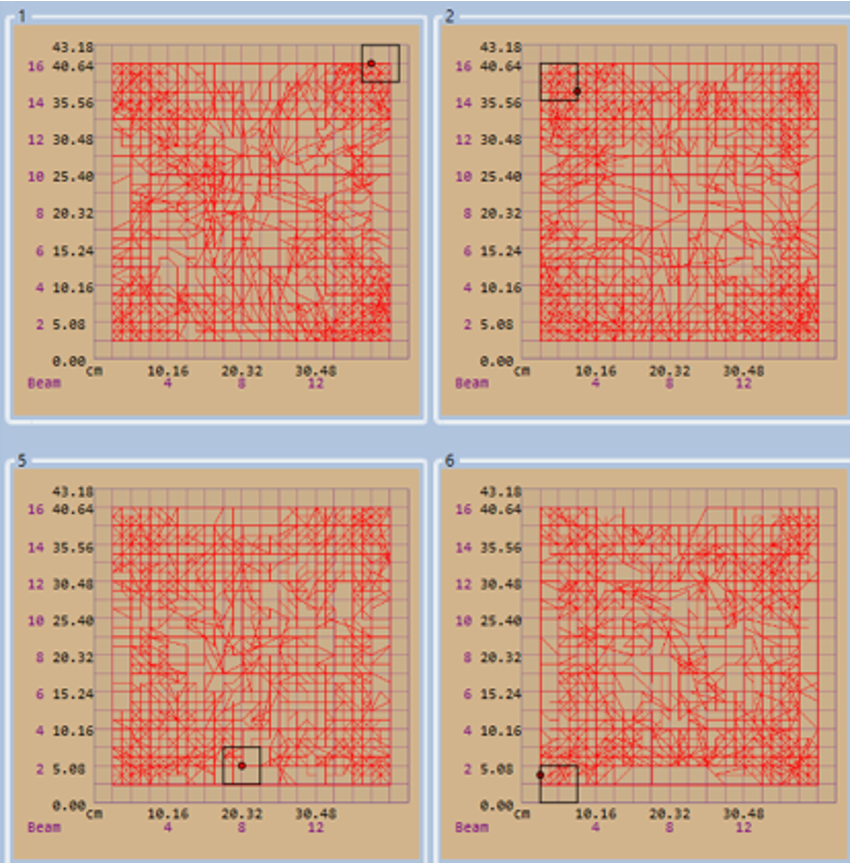
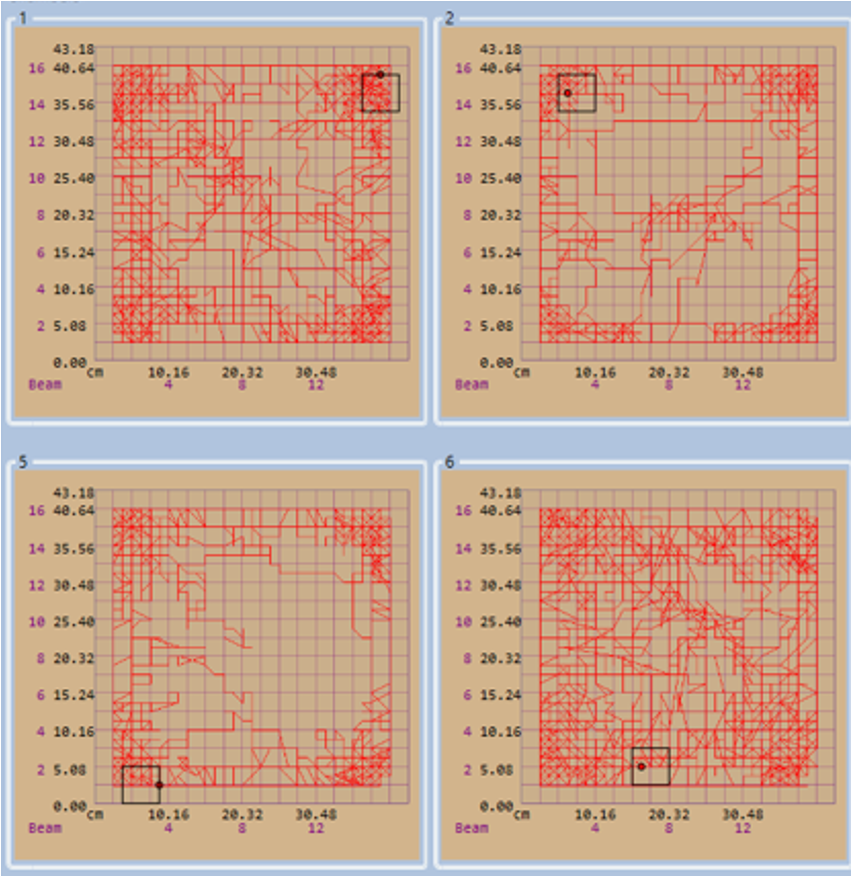
Motor Function – Rotarod
ARTE10 animals show no motor function deficits using the rotarod at 5 months of age.

Motor Function - Running Wheel (20 hour recordings)
The running wheel provides information about natural activity levels during the animal's dark and light phases. ARTE10 mice are naturally hyperactive in the running wheel. This data supports the hypothesis that LMA hypoactivity may be anxiety related.

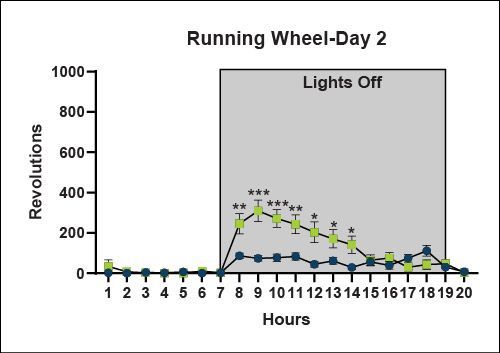
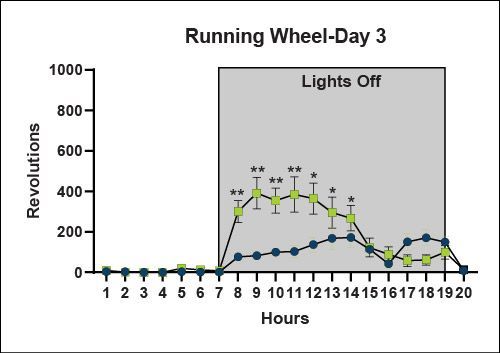

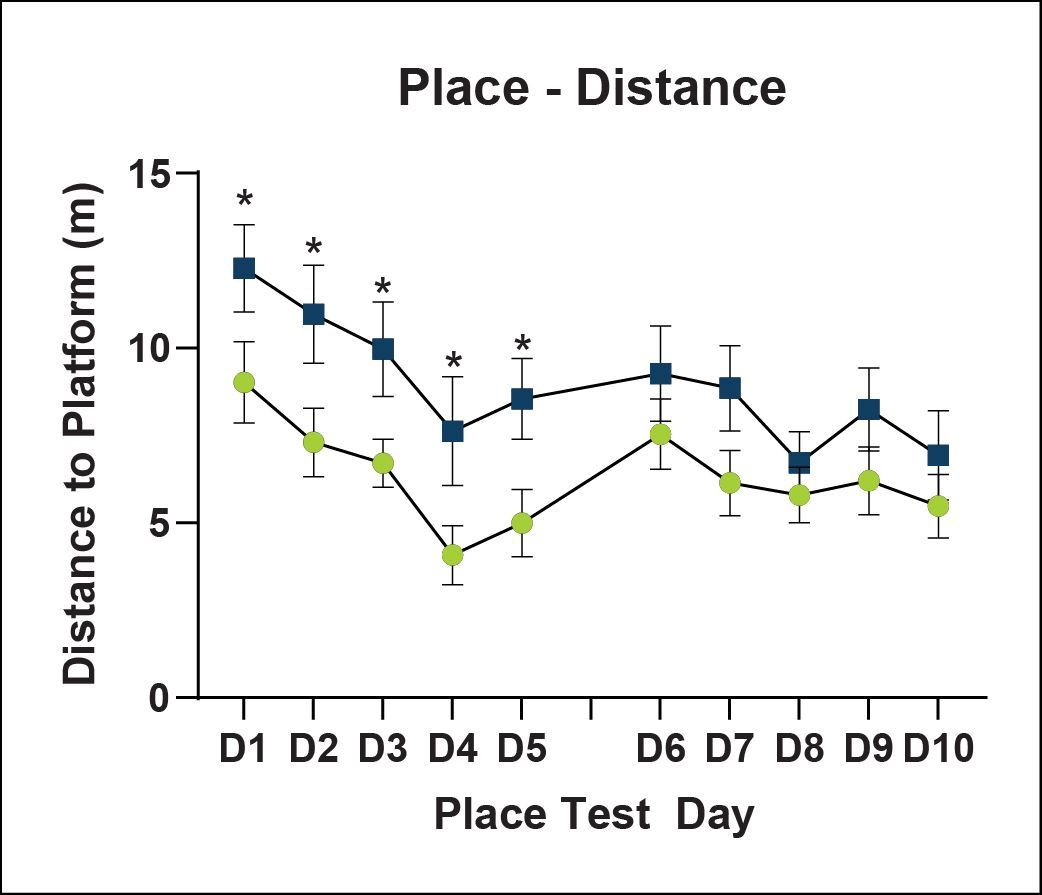
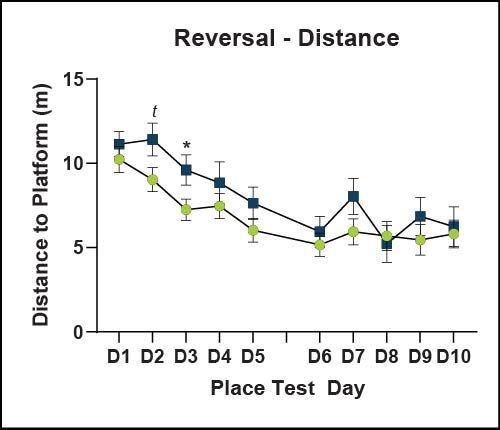
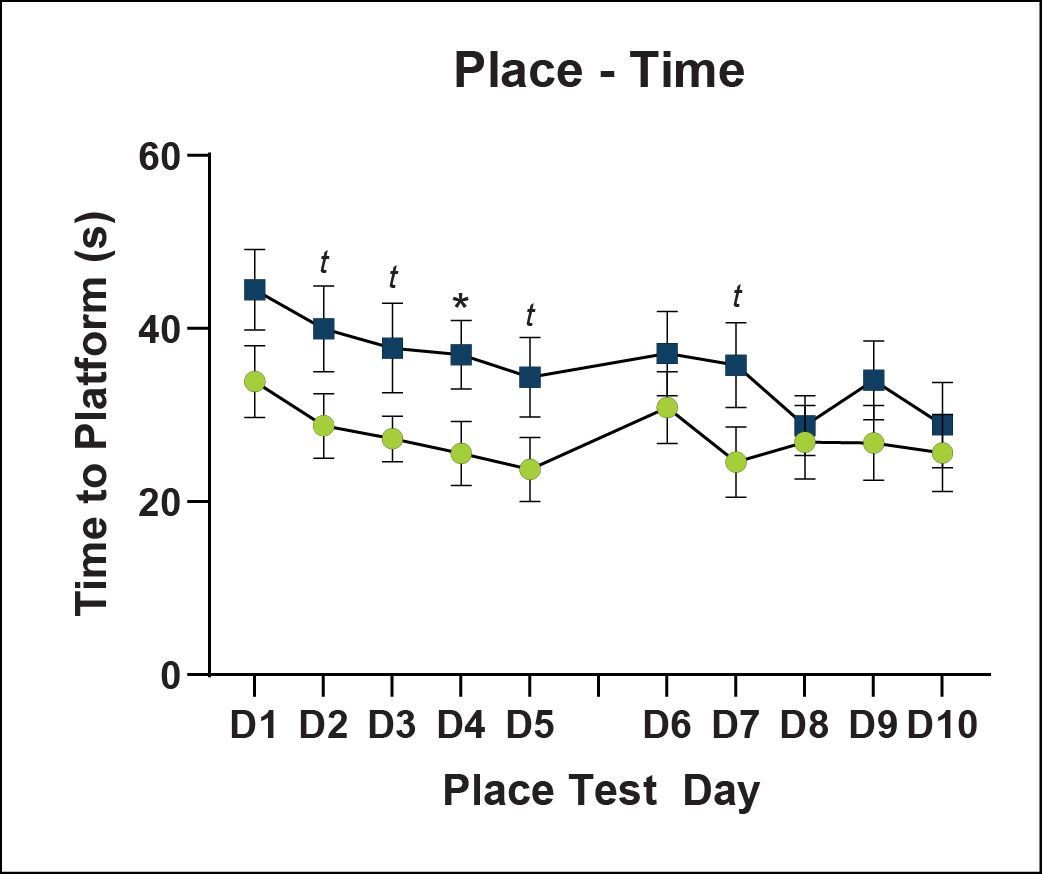
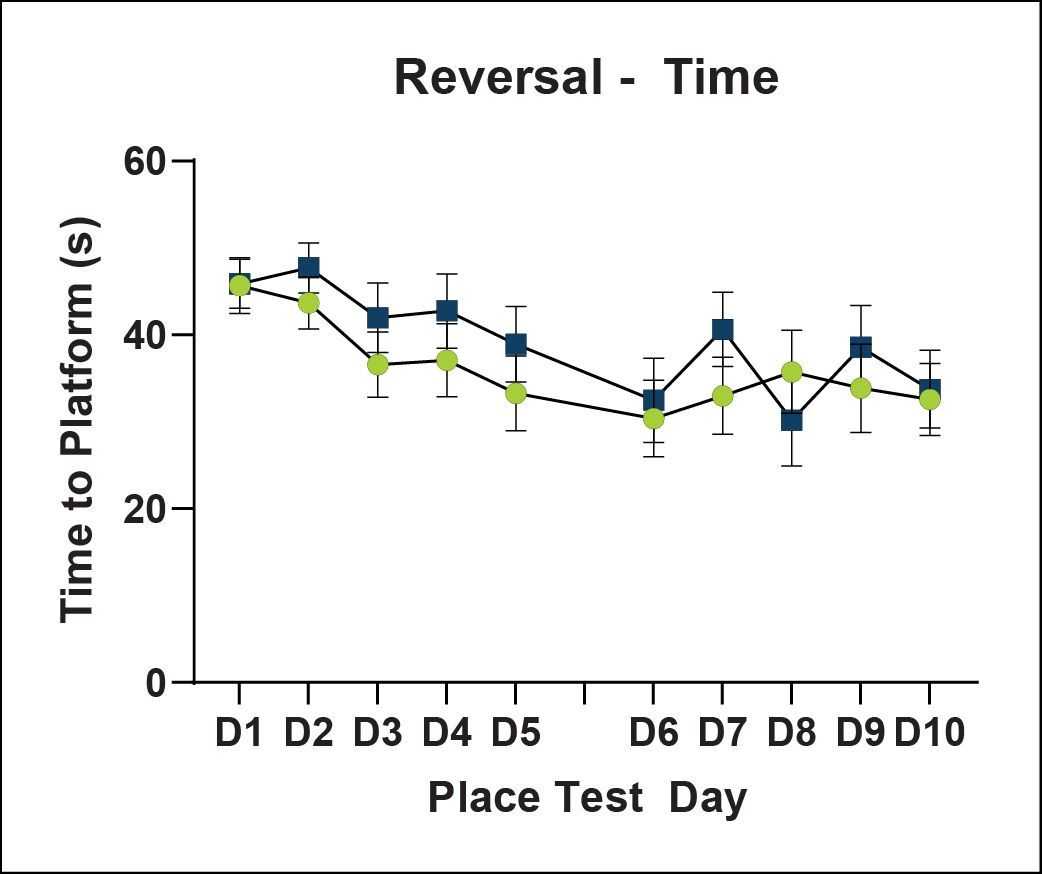
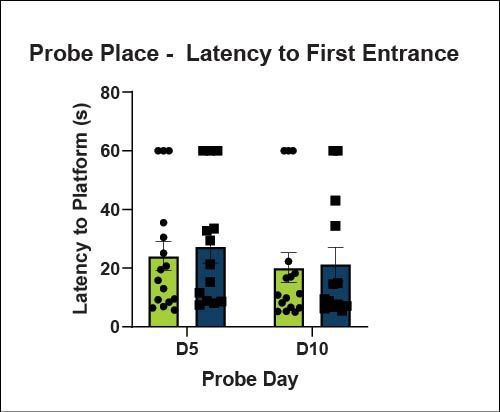
Learning and Memory - Morris Water Maze
Spatial learning is impaired in cued and place learning in ARTE10 mice. No differences in working memory were found during the probe test. Reversal learning was partially impaired in ARTE10 mice.




| Indication | ARTE10 Effect | Test | Significant |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anxiety | ↑ | Canopy Test | ARTE10 – increased anxiety like behaviour |
| Motivation/Mood | ↓ | Nest Building | Decreased motivation/mood |
| Sensory Motor gating | ↓ | PPI | Deficits in sensory motor gating |
| Activity | ↓ | LMA | Hypolocomotion or open field showing anxiety to enter centre |
| Motor Function | NS | Rotarod | No motor impairments |
| Activity | ↑ | Running Wheel | Hyperactive |
| Learning | ↓ | MWM | Spatial learning deficit |
| Memory | NS | MWM | No spatial working memory impairment |
Biomarkers

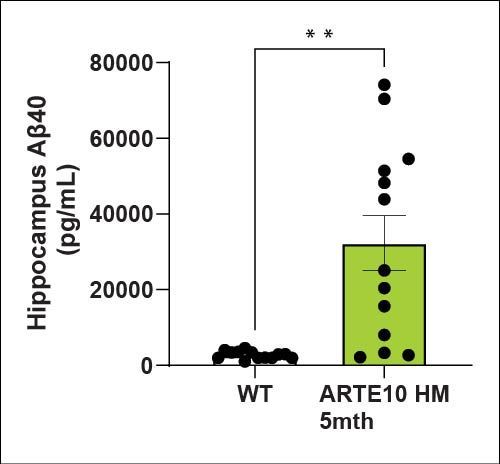
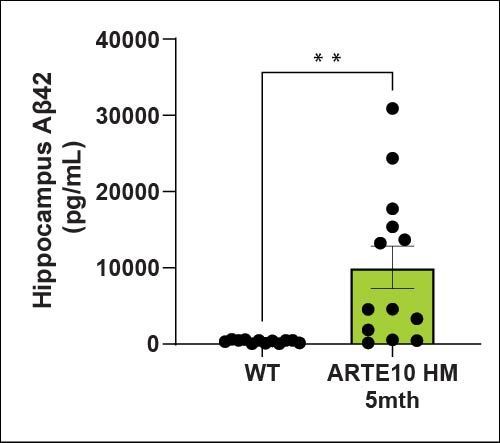
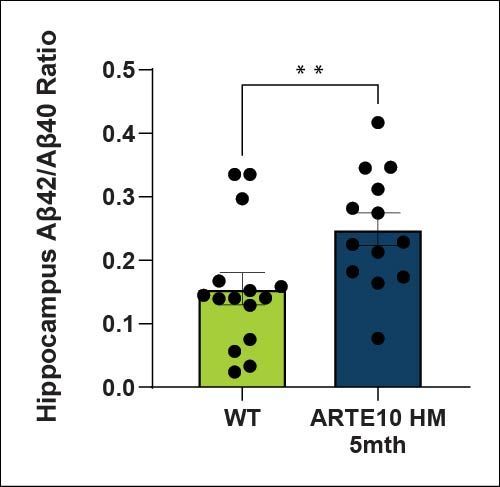
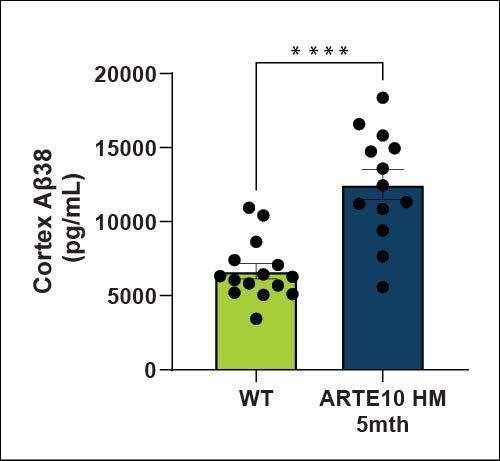
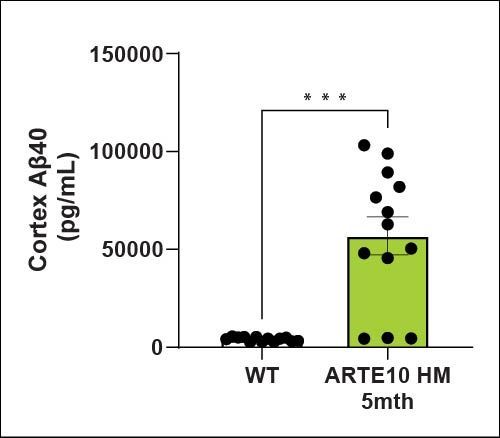
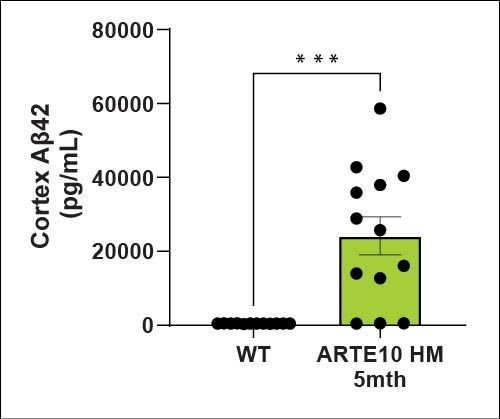
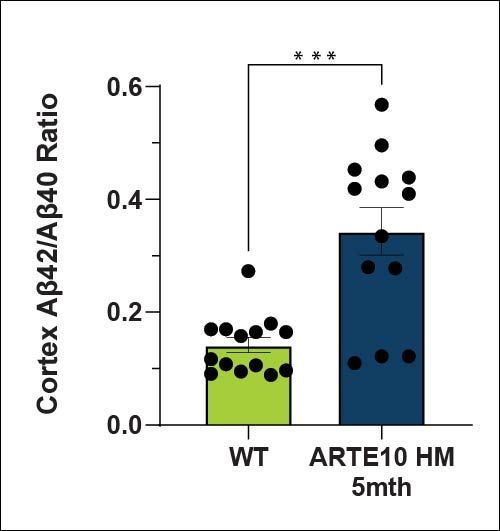
Amyloid levels (Aβ40 and Aβ42) are increased in the cortex and hippocampus of ARTE10 animals as expected. There is a higher amyloid load in the cortex than the hippocampus at 5 months of age.

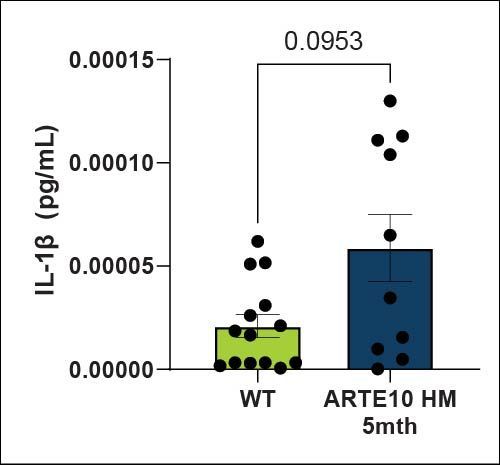
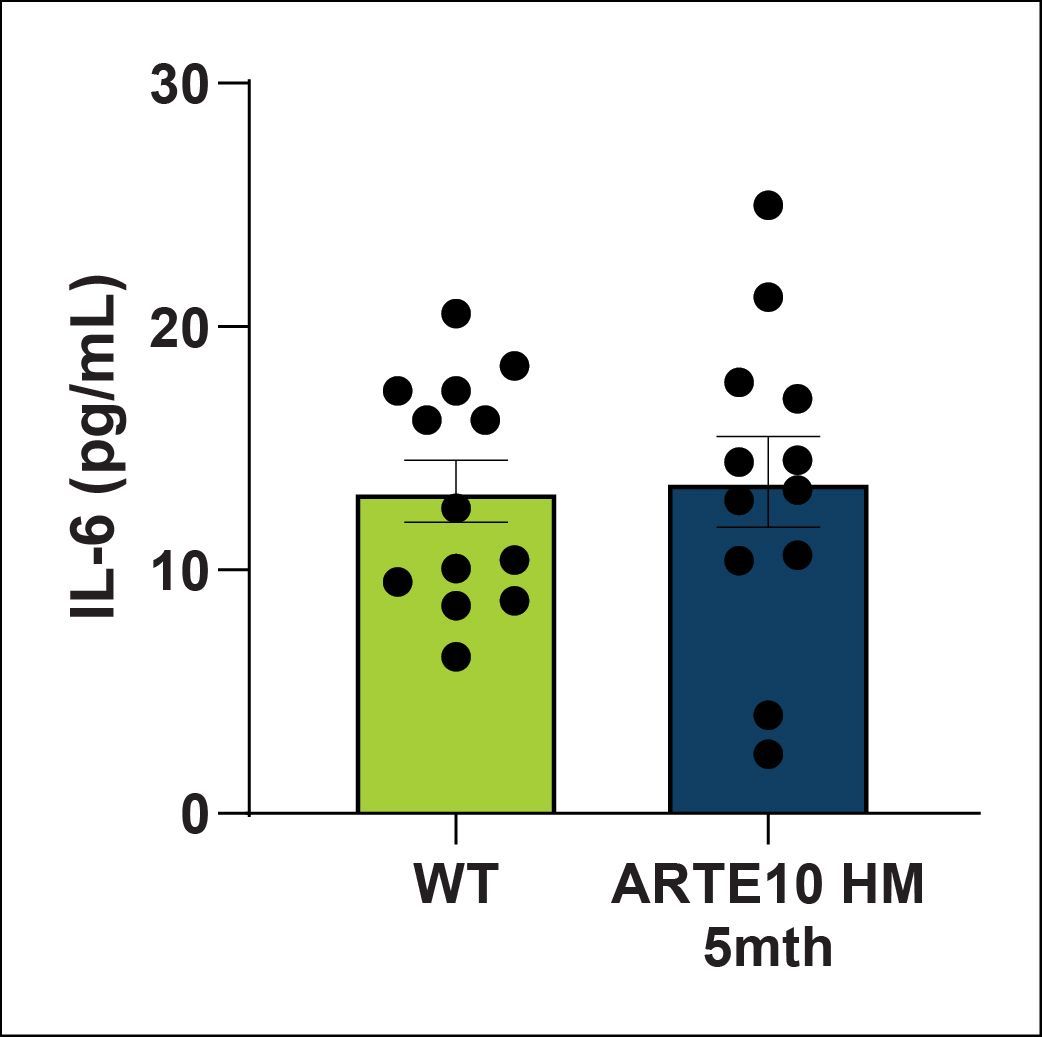

IFNγ, lL-1β, IL-6 and TNFα levels in plasma were quantified using a MSD kit. Cytokine levels are starting to increasing at this stage with trend level or significant effects in IFNγ, IL-1β and TNFα. Increased cytokines indicates increased inflammatory processes are present in the ARTE10 animals.

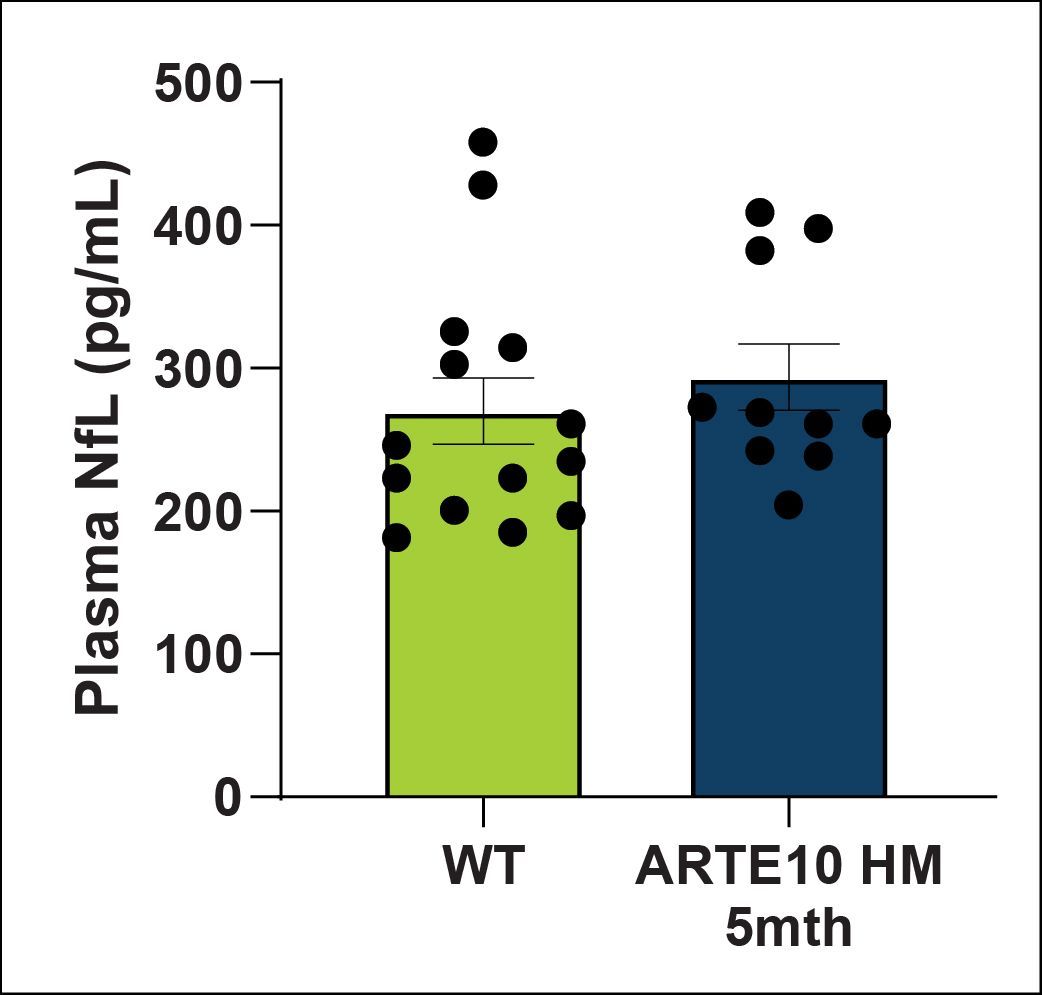
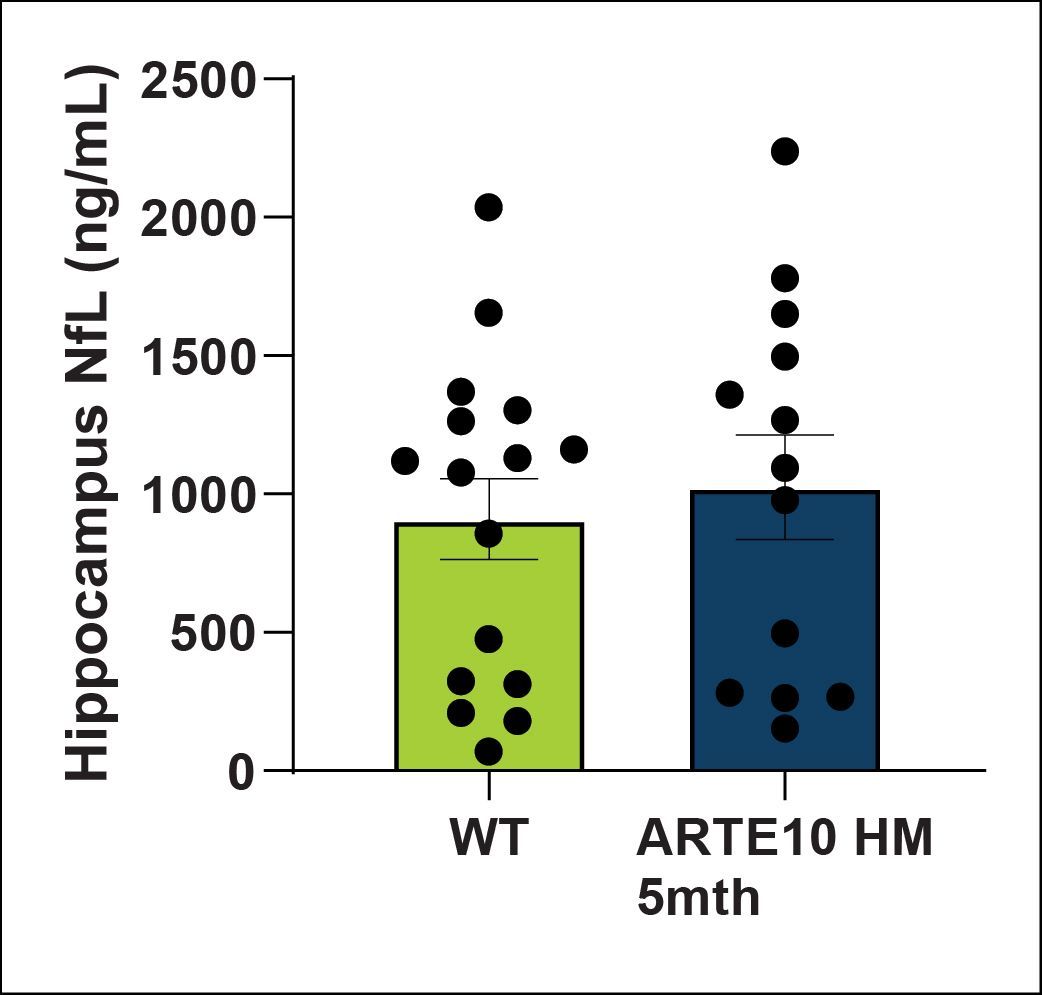
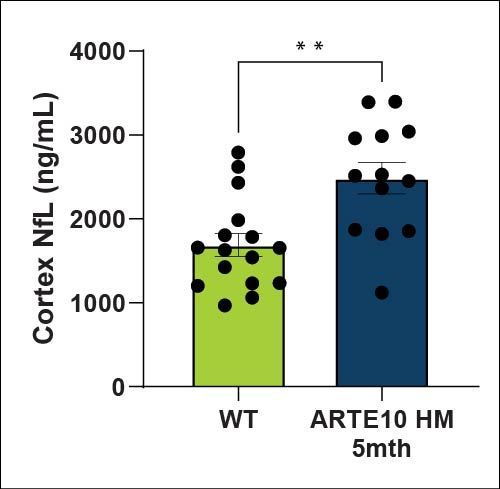
NfL levels in plasma, CSF, hippocampus and cortex were quantified using a MSD kit. NfL is a biomarker for neuronal damage. NfL levels are trending towards an increase in the CSF of ARTE10 animals at 5 months of age. No significant changes in plasma or brain were detected.
| Biomarker | Sample Type | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| NfL | Plasma | NS |
| CSF | Trending ↑ | |
| Hippocampus | NS | |
| Cortex | ↑ | |
| IFNγ | Plasma | NS |
| IL-1β | Plasma | Trending ↑ |
| IL-6 | Plasma | NS |
| TNFα | Plasma | ↑ |
| Aβ40 | Hippocampus | ↑ |
| Cortex | ↑ | |
| Aβ38 | Hippocampus | NS |
| Cortex | ↑ | |
| Aβ42 | Hippocampus | ↑ |
| Cortex | ↑ | |
| Aβ42/Aβ40 Ratio | Hippocampus | ↑ |
| Cortex | ↑ |
- Grewal S.S., Shepard J.K., Bill D.J., Fletcher, A. and Dourish C.T. 1997. Behavioural and pharmacological characterization of the canopy stretched attend posture test as a model of anxiety in mice and rats. Psychopharmacology. 133:29-38
- Jacobson ML, Wulf HA, Tsuda MC, Browne CA, Lucki I. Sex differences in the modulation of mouse nest building behavior by kappa opioid receptor signaling. Neuropharmacology. 2020 Oct 15;177:108254. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108254. Epub 2020 Jul 26. PMID: 32726598; PMCID: PMC11423493.